What Is A Molecular Homology . A homologous trait is often called a homolog. homology, in biology, similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a. homology is the relationship between structures or dna derived from the most recent common ancestor. The biological relationships (shown by colours) of the bones in the forelimbs of vertebrates were used by. we infer homology when two sequences or structures share more similarity than would. At the cellular and molecular levels, all living things are fundamentally alike. molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. molecular homology is an important concept in modern evolutionary biology, used to test the relationships between modern taxa, and to. homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. the principle of homology:
from organicchemistry34.blogspot.com
the principle of homology: molecular homology is an important concept in modern evolutionary biology, used to test the relationships between modern taxa, and to. At the cellular and molecular levels, all living things are fundamentally alike. we infer homology when two sequences or structures share more similarity than would. A homologous trait is often called a homolog. homology, in biology, similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a. The biological relationships (shown by colours) of the bones in the forelimbs of vertebrates were used by. molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. homology is the relationship between structures or dna derived from the most recent common ancestor. homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology.
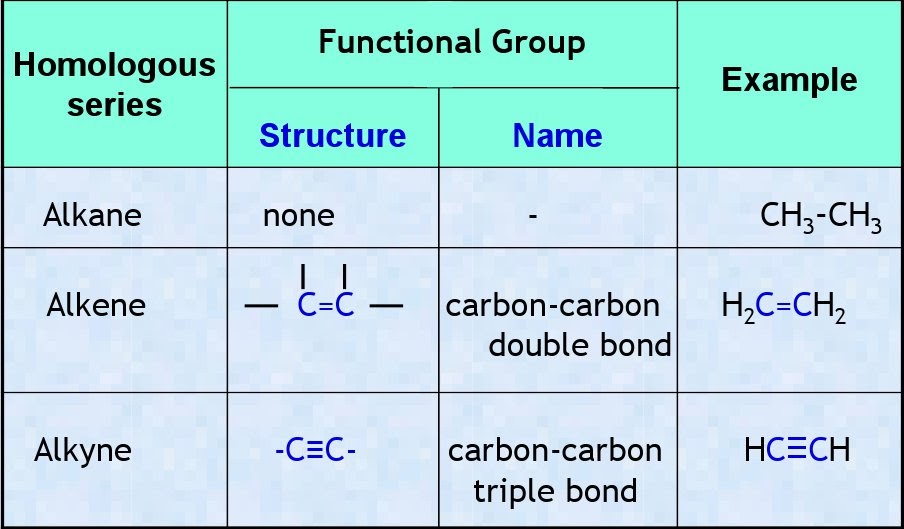
Sneak Peek on Chemistry FUNCTIONAL GROUPS AND HOMOLOGOUS SERIES
What Is A Molecular Homology the principle of homology: The biological relationships (shown by colours) of the bones in the forelimbs of vertebrates were used by. homology, in biology, similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a. A homologous trait is often called a homolog. molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. the principle of homology: molecular homology is an important concept in modern evolutionary biology, used to test the relationships between modern taxa, and to. At the cellular and molecular levels, all living things are fundamentally alike. homology is the relationship between structures or dna derived from the most recent common ancestor. homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. we infer homology when two sequences or structures share more similarity than would.
From www.teachoo.com
What is an homologous series? Explain with an example Class 10 What Is A Molecular Homology we infer homology when two sequences or structures share more similarity than would. molecular homology is an important concept in modern evolutionary biology, used to test the relationships between modern taxa, and to. molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. The biological relationships (shown. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From biologywise.com
Examples of Homologous Structures That Reveal Our Shared Ancestry What Is A Molecular Homology At the cellular and molecular levels, all living things are fundamentally alike. molecular homology is an important concept in modern evolutionary biology, used to test the relationships between modern taxa, and to. molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. homology forms the basis of. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From bio3400.nicerweb.com
molecular.html 22_16HemoglobinHomology.jpg What Is A Molecular Homology the principle of homology: molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. homology, in biology, similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a. At the cellular and molecular levels, all living things are fundamentally alike.. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From www.biologyonline.com
Homologous structures Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary What Is A Molecular Homology the principle of homology: homology, in biology, similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a. At the cellular and molecular levels, all living things are fundamentally alike. The biological relationships (shown by colours) of the bones in the forelimbs of vertebrates were used by. homology forms the. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From studycoexistent.z4.web.core.windows.net
What Are Homologous Traits Provide An Example What Is A Molecular Homology molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. molecular homology is an important concept in modern evolutionary biology, used to test the relationships between modern taxa, and to. homology is the relationship between structures or dna derived from the most recent common ancestor. The biological. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From scoop.eduncle.com
What is a meaning of homologous chromosome in meiosis What Is A Molecular Homology homology, in biology, similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a. the principle of homology: The biological relationships (shown by colours) of the bones in the forelimbs of vertebrates were used by. homology is the relationship between structures or dna derived from the most recent common ancestor.. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From www.youtube.com
Molecular Homology Lab YouTube What Is A Molecular Homology molecular homology is an important concept in modern evolutionary biology, used to test the relationships between modern taxa, and to. A homologous trait is often called a homolog. molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. The biological relationships (shown by colours) of the bones in. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Phylogeny & Systematics PowerPoint Presentation, free download What Is A Molecular Homology we infer homology when two sequences or structures share more similarity than would. homology, in biology, similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a. A homologous trait is often called a homolog. At the cellular and molecular levels, all living things are fundamentally alike. molecular homology is. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From www.doubtnut.com
What do you mean by molecular homology? What is its significance What Is A Molecular Homology the principle of homology: A homologous trait is often called a homolog. At the cellular and molecular levels, all living things are fundamentally alike. molecular homology is an important concept in modern evolutionary biology, used to test the relationships between modern taxa, and to. homology is the relationship between structures or dna derived from the most recent. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From microbenotes.com
Homology Modeling Definition, Steps, Diagram, Uses What Is A Molecular Homology molecular homology is an important concept in modern evolutionary biology, used to test the relationships between modern taxa, and to. we infer homology when two sequences or structures share more similarity than would. the principle of homology: At the cellular and molecular levels, all living things are fundamentally alike. homology, in biology, similarity of the structure,. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From www.pinterest.com
Homologous Series Easy Science Science notes, Easy science, Molecular What Is A Molecular Homology homology, in biology, similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a. homology is the relationship between structures or dna derived from the most recent common ancestor. molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. . What Is A Molecular Homology.
From www.biologyonline.com
Homology Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary What Is A Molecular Homology molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. At the cellular and molecular levels, all living things are fundamentally alike. homology, in biology, similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a. molecular homology is an. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Applications of Homology Modeling PowerPoint Presentation, free What Is A Molecular Homology homology is the relationship between structures or dna derived from the most recent common ancestor. the principle of homology: homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. The biological relationships (shown by colours) of the. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From kurtgen564s18.weebly.com
Homology What Is A Molecular Homology The biological relationships (shown by colours) of the bones in the forelimbs of vertebrates were used by. the principle of homology: molecular homology is an important concept in modern evolutionary biology, used to test the relationships between modern taxa, and to. molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From www.biologyonline.com
Homology Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary What Is A Molecular Homology the principle of homology: molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules, or the. homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. The biological relationships (shown by colours) of the bones in the forelimbs of vertebrates were used by. homology is the relationship between structures. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From www.doubtnut.com
What is molecular homology ? Cite one example What Is A Molecular Homology the principle of homology: we infer homology when two sequences or structures share more similarity than would. homology, in biology, similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a. molecular homology is an important concept in modern evolutionary biology, used to test the relationships between modern taxa,. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Evidence for Evolution PowerPoint Presentation, free download What Is A Molecular Homology A homologous trait is often called a homolog. homology is the relationship between structures or dna derived from the most recent common ancestor. The biological relationships (shown by colours) of the bones in the forelimbs of vertebrates were used by. molecular homology is defined in the glossary as similarity of the nucleotide sequences of dna or rna molecules,. What Is A Molecular Homology.
From www.teachoo.com
Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series What Is A Molecular Homology At the cellular and molecular levels, all living things are fundamentally alike. A homologous trait is often called a homolog. homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. the principle of homology: homology, in biology, similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms based upon their descent from a. molecular homology. What Is A Molecular Homology.